Everything You Need to Know About Low Back Pain from an Eagan Chiropractor
Overview of Low Back Pain
Anatomy
Understanding your spine and how it works can help you better understand low back pain. Patient education surrounding low back pain is important because it helps to alleviate the fear and anxiety that can accompany this type of pain. Your spine is made up of bones, muscles, ligaments, and intervertebral disks. The bones provide the structure for your spine, while the muscles and ligaments help to stabilize the bones. The intervertebral disks provide "cushioning" to the spine, allowing it to tolerate various movements and stressors. The nerves that allow communication between your brain and your body are also located inside the spine.
While low back pain will always feel like an inconvenience, it is important to remember that it is very common and will likely resolve on its own.
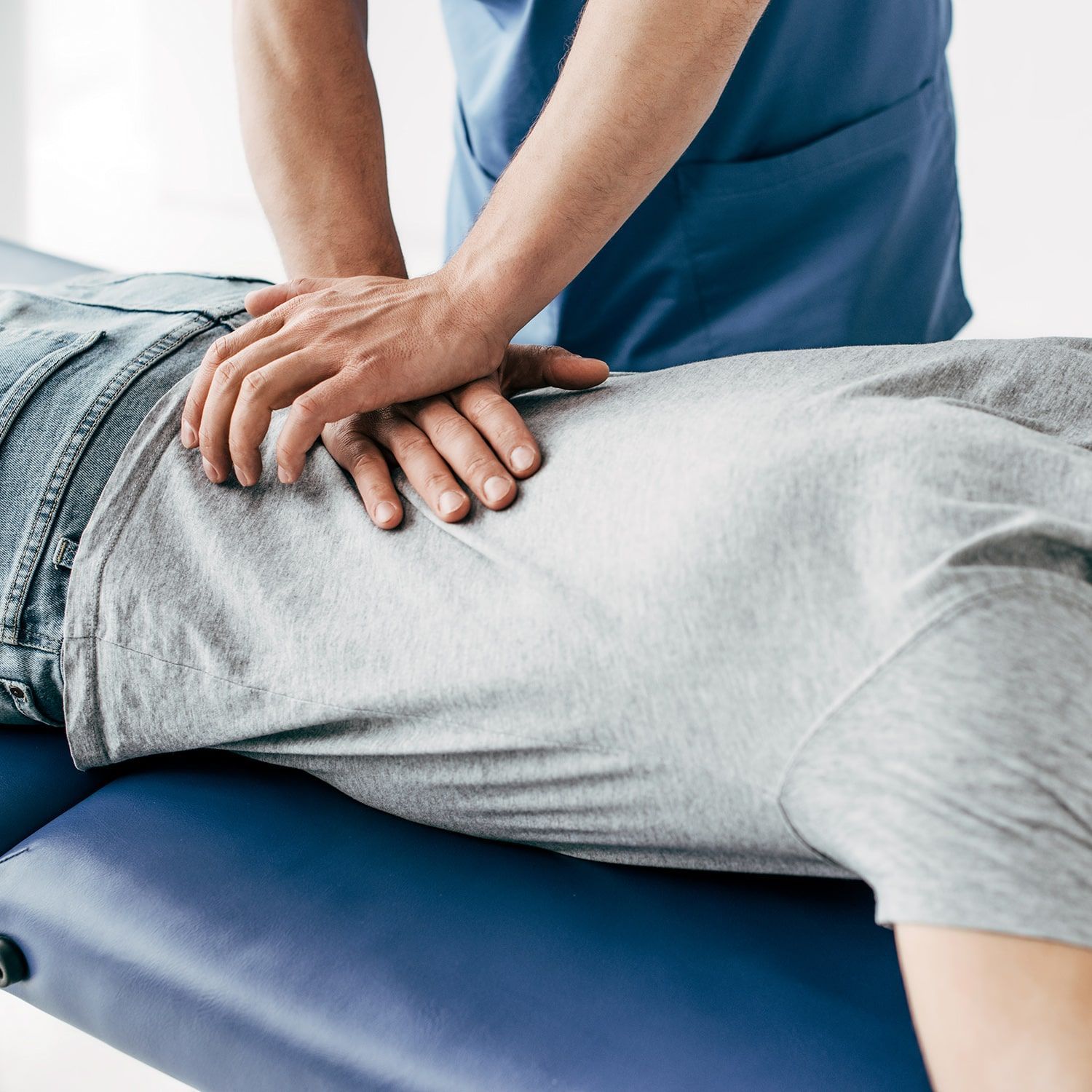
What Exactly Is the Low Back, Anyway?
The low back, also called the lumbar spine, is the largest region of the spine. It's made up of five vertebrae and two facet joints at each level. The low back carries the weight of the entire torso and allows for all the movements in our day-to-day lives. While it is an astonishing design, it is also susceptible to injuries and pain.
Lower back pain is a common complaint in America, with an estimated 25% of adults experiencing low back pain. Chronic low back pain can be caused by wear and tear on the spine or injuries, such as a herniated disk. Lower back pain is commonly experienced as a dull ache and muscle spasms in the hips and/or pelvis, sharp tingling pain that starts in your lower back, or sciatica. Lower back pain can feel like it comes and goes - flaring up now and then but generally getting progressively worse over time. The underlying cause of lower back pain is often unknown. Lower back pain symptoms are not one-size-fits-all, and vary by person.
What are the most common causes of low back pain?
Over-activity
One of the most common cause of low back pain is over activity. This can be from too much activity or from activities that the body is not used to doing on a normal basis. Muscle soreness is often brought on by over-activity of muscles and ligaments during the first few days of a sport season, or too much work in one specific position.
Arthritis
Arthritis is a common cause of low back pain. There are many different types of arthritis, but some of the most common types are degenerative arthritis (Osteoarthritis), rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis. Osteoarthritis is the most common to affect the low back.
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative condition of the joints in which cartilage breaks down and causes pain, stiffness and loss of movement. It can affect any joint but it commonly affects the low back. This type of arthritis can be caused by age, injury, or congenital conditions.
Muscle or ligament strain
Another common cause of lower back pain is straining a muscle or spraining a ligament. A muscle strain occurs when your muscles are overloaded and tear/strain. A ligament sprain occurs when the ligaments that support your spine are overstretched or overloaded. Both muscle strains and ligament sprains can be caused by a sudden movement, lifting something heavy, or repetitive motions. Ice, heat, and avoiding strenuous activity are all ways to help alleviate the pain while allowing time for the muscle sprain or ligament strain to heal. Your chiropractor will be able to give you specific remedies for lower back pain based on the type of injury that caused it.
Joint dysfunction
The facet joints are the joints in your spine that connect your vertebrae together. When these joints become dysfunctional, it can lead to inflammation, stiffness, and pain. Sciatica is a condition that is caused by irritation in the nerves that form the sciatic nerve. This nerve is formed from spinal nerves that exit the spinal cord in the low back. When it becomes irritated, it can cause pain in your lower back that radiates down through your legs.
Back pain can be brought on by everyday movements. For example, if you sit at a desk all day, you may start to experience back pain after a while. This is because your muscles and joints have gotten stiff due to lack of motion while you sit. The causes of back pain vary, but one of the most common sources is a repetitive motion injury to the upper back or neck. This type of injury is often caused by poor posture or ergonomics.

Disk Injury
A slipped or herniated disk is one of the most common causes of low back pain. A herniated disk occurs when a tear occurs in the outside of the disk structure, sometimes allowing the nucleus to push through. A slipped or herniated disk may not result in low back pain, but it can lead to radiating pain that affects everyday life. The pain often radiates from the buttock down the leg and foot, which is often times referred to as sciatica. Herniated disks are often caused by lifting, pulling, bending or twisting movements. These activities put stress on the disk and may cause the nucleus to slip through the annulus.
What is the prognosis for people with low back pain?
Most people with acute low back pain improve quickly
On average, an episode of acute low back pain can last up to 3 months. If you have had low back pain for more than 6 weeks, your doctor may consider ordering an imaging test such as an X-ray or MRI to check whether there is a serious underlying cause for your pain, such as a herniated disc or bone spurs.
Acute low back pain is often caused by muscle strains and spasms. These can be treated with a variety of treatments, including:
- Staying active without continuing to aggravate your back pain
- Exercise
- Spinal manipulation
Bed rest is not recommended for most acute low back pain cases. Exercise is an effective way to speed recovery and strengthen the back muscles. Spinal manipulation may be helpful for some patients with acute low back pain.
Most people with chronic low back pain improve with treatment
Chronic low back pain is defined as pain that persists for more than six months. There are a wide variety of ways to manage chronic low back pain. The goal of treatment is to help the patient find a way to manage their level of pain, rather than letting the pain become debilitating.
"Graded exercise" is an effective way to work through pain in a gradual manner and get back into to the activities you enjoy.
Exercise is an effective way to speed recovery and help strengthen the back and abdominal muscles. In addition, exercises can help reduce the risk of returning to back pain.
Timeline for recovery
There are three phases of recovery from an injury: the acute phase, the subacute phase, and the chronic phase.
- The acute phase of an injury is the first few days or weeks. This is when the pain is the worst and the person is at the greatest risk for further injury. During this phase, it is important to minimize activities that aggravate the pain while attempting to stay active as much as possible. In addition, things like ice, heat, light stretching, and walking can be helpful during this phase.
- The subacute phase of an injury lasts for a few weeks to a few months. This is when the person begins to slowly return to their normal activities. They may still have some pain and discomfort, but it should be manageable and improving over time.
- The chronic phase of an injury is when the person has fully recovered and is back to their normal activities. They may still have some residual pain and discomfort, but it should not be severe.
Most people will experience low back pain at some point in their lives. The average duration of an episode of low back pain is about six weeks.
Who's at Risk for Low Back Pain?
Athletes and low back pain
Low back pain occurs in roughly 10-15% of young athletes. This can be due to many factors including:
- Ineffective warm-ups
- Overuse with not enough rest between activities
- Repetitive movements such as repeated flexion, extension, and torsion, which are frequently performed in gymnastics, ice skating, and dancing.
- Acute traumatic event commonly seen in individuals participating in sports such as football, rugby, gymnastics, ice skating, and dancing.
Elderly and low back pain
As people age, they are more likely to experience low back pain. There are a number of reasons for this. The older we become, the more our bones and muscles weaken. This can lead to problems with balance and coordination, which can make falls more likely. Falls can cause injuries that lead to low back pain. This is why it is so important to continue resistance training to some degree as we age. In addition, the disks in our spine begin to degenerate. This can lead to a condition called disk degenerative disease, which can be very painful. Another possible injury occurring in the senior population is a compression fracture which can occur due to inadequate bone density. Finally, as we age, we are more likely to develop arthritis. Arthritis can cause pain and stiffness in the joints, including the joints in the spine.
There are a number of things that you can do to reduce your risk of developing low back pain. First, you can maintain a healthy weight. This will help to reduce the strain on your back. Second, you can exercise regularly. This will help to keep your muscles strong and your joints flexible. Third, you can use proper lifting techniques. When lifting heavy objects, be sure to bend at the knees, not the waist. Fourth, you can wear comfortable, supportive shoes. High heels and flip-flops should be avoided.
Treatment Options for Low Back Pain
Chiropractic
Chiropractors are health care professionals who focus on the diagnosis and treatment of neuromusculoskeletal disorders, with an emphasis on the spine. Chiropractic adjustment is a common treatment option for low back pain. Chiropractic adjustments aim to restore normal function to the spine and nervous system, which can reduce pain and improve overall function.

Stretching and exercises
Stretching your back before and after exercising is a great way to avoid injury. Swimming and walking are good exercises for those who want to improve their general fitness and help prevent back pain while not over-straining their joints. Further blog posts will offer some ideas for getting started with exercise!
Massage Therapy
Massage therapy may be effective at alleviating low back pain in certain cases. Massage therapy targets the muscle tissues and attempts to help alleviate the stiffness and soreness. The therapist will use their hands to apply pressure to the affected areas.
There are different types of massage therapy, and the type that is best for you will depend on your specific situation. Swedish massage is a common type of massage that uses long strokes and gentle pressure to relax the muscles. Deep tissue massage is another type that uses more intense pressure to reach the deeper layers of muscle tissue.
If you are considering massage therapy as a treatment option for your low back pain, it is important to consult with your doctor first. They can help you determine if massage therapy is right for you and can also provide referrals to reputable therapists in your area.
Prevention
Exercise Regularly
A combination of aerobic exercise and strength training can help prevent low back pain. Regular exercise helps maintain good posture and a healthy weight, both of which are important for preventing back pain. Back exercises specifically can help strengthen the muscles that support the spine and prevent lower back pain.
Use Proper Lifting Technique
One of the best ways to prevent back pain is to use proper lifting technique. When lifting heavy objects, it's important to keep your back straight and avoid twisting. You should also keep the load close to your body and take breaks frequently. If you're lifting something really heavy, it's best to find a lifting partner or spotter.
Another way to prevent back pain is regular aerobic exercise. This will help increase your strength and endurance, which can lead to better back function. Additionally, muscle-building exercises are good for maintaining a strong core. A strong core helps prevent back injuries and strains from lifting heavier objects or kneeling on the ground too often.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is important for overall health and well-being. Being overweight or obese can lead to a number of health problems, including heart disease, diabetes, and joint pain. Every pound you gain puts a strain on your musculoskeletal system, which consists of your bones, joints, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, and muscles. This can cause joint pain and other problems. In addition, excess weight pushes the pelvis forward and thereby strains the lower back. This can lead to back pain and other problems. To maintain a healthy weight, eat a nutritious diet and get regular exercise. These lifestyle changes will help you lose weight and keep it off.
Avoid Smoking
Smoking increases the risk of back pain. The chemicals in cigarettes damage the spine and other bones in the body. These chemicals also increase inflammation, which can lead to pain. Avoid smoking and maintain a healthy weight to prevent back pain or its recurrence.
Avoid Sitting for Long Periods of time
Sitting for long periods of time can be a common cause of low back pain. To prevent or avoid lower back pain, it is important to learn good posture and to strengthen the muscles in the back. The best posture is the next posture. This means that the goal should always be to change postures frequently and not stay in any one position for hours. When sitting, it is important to keep the spine in a neutral position. The spine should not be arched forward or rounded backward.
Some other tips for avoiding lower back pain when sitting include:
- Use a small pillow or rolled-up towel to support the natural curve of your spine.
- Place your feet on a footrest or stool to keep your knees and hips at a 90-degree angle.
- Adjust your chair height so that your thighs are parallel to the ground and your feet are flat on the floor.
- Get up and move around every 30 minutes to hour.

